Nuclear Imaging Consultation Service


|
Location
|
: Nuclear Imaging Unit, Hospital Sultan Abdul Aziz Shah (HSAAS)
|
|
Time
|
: Monday – Friday / 8.30 am – 4.30 pm
|
|
Medical Officer
|
: Dr. Ahmad Danial bin Ahmad Shahrir
|
|
|
|
Dr. Khairul Aliff bin Khairuman
|
|
Tel. No.
|
: 03-97695 9563 / 9564
|
|
Email
|
:
|
nuclearimaging_hsaas@upm.edu.my
|
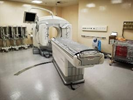
SPECT - CT SCAN
|
A single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) scan lets your doctor analyze the function of some of your internal organs. A SPECT scan is a type of nuclear imaging test, which means it uses a radioactive substance and a special camera to create 3-D pictures. SPECT scan produces images that show how your organs work. For instance, a SPECT scan can show how blood flows to your heart or what areas of your brain are more active or less active. Nuclear Imaging Unit HSAAS use GE Discovery NM/CT 670 SPECT/CT system with 16-slice CT. This system has the capability to shorten acquisition times, improve dose management, and enable more convenient patient scheduling in comparison to separate, conventional SPECT and CT exams. The imaging time is reduced to as little as 25 minutes. This reduction in time can be less painful, and possibly reduce patient movement due to the pain or uncomfortable positioning, minimizing artifacts in the scan. A shorter, more comfortable scan also has the potential to improve image quality, allowing clinicians to be more confident in their diagnosis.
|
|
Name of scan
|
Purpose of scan
|
|
Whole body bone scan
|
Evaluate bone pathologies
|
|
Thyroid scan
|
Assess thyroid function
Evaluate thyroid nodule
|
|
Renal DTPA / MAG3
|
Determine kidney function
Evaluate urinary obstruction or reflux
Transplant kidney assessment
|
|
Sentinel node scintigraphy
|
Identify first drainage node before breast surgery
|
|
Myocardial perfusion
|
Detect ischemic heart disease
Determine living heart cell (viability)
|
|
Renal DMSA
|
Evaluate scar area in the kidney from infection or trauma
Determine differential kidney function
|
|
Parathyroid scan
|
Localize active parathyroid tumour (adenoma)
|
|
Radioactive iodine
Whole body scan
|
Detect residual, recurrent of thyroid cancer
|
|
Meckel's Diverticulum Scan
|
Heterotopic gastric mucosa in Meckel's diverticulum
|
|
HIDA scan
|
Evaluation suspected biliary atresia
To detect bile duct obstruction, cholecystitis
|
|
Theranostics Clinic:
In Nuclear Medicine, the theranostic approach is an established tool for specific molecular targeting both for diagnosis and therapy. The diagnosis of thyroid disorders and therapy have an important role in the practice of Nuclear Medicine. Radioiodine is still the primary therapy for Grave's disease, toxic nodular goiter and standard therapy for differentiated thyroid cancer ( DTC).
|
| |
|
Role of Iodine-131 in DTC
Majority of DTC like papillary and follicular are cured by means of surgical resection and radioiodine therapy. The traditional imaging approach for follow-up of the large proportion of patients with DTC who are at low risk for residual or recurrent disease were namely Iodine-131 whole-body scintigraphy (WBS) and serial serum thyroglobulin (Tg) testing. Role of Iodine-131 in hyperthyroidism like Grave's disease and toxic nodular goiter have been treated successfully with Iodine-131 therapy, which is now the treatment of choice in majority of patients. The effectiveness of radioiodine treatment for hyperthyroidism is due to radiation induced cellular damage resulting from high-energy beta emission.
|
   |
|
Hot Labs
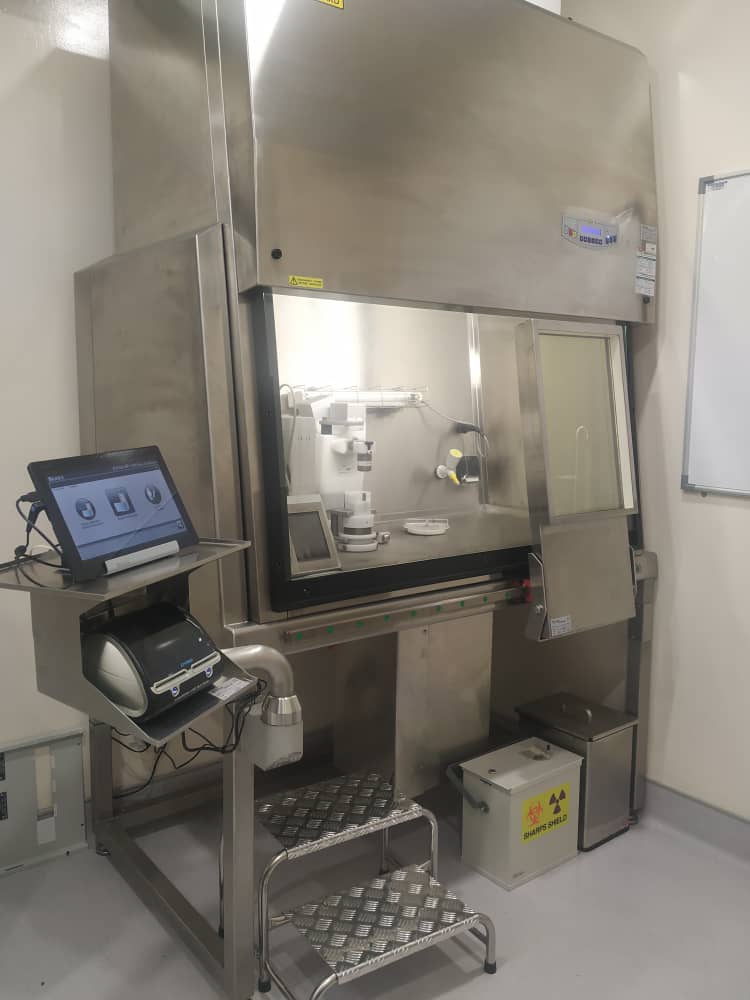
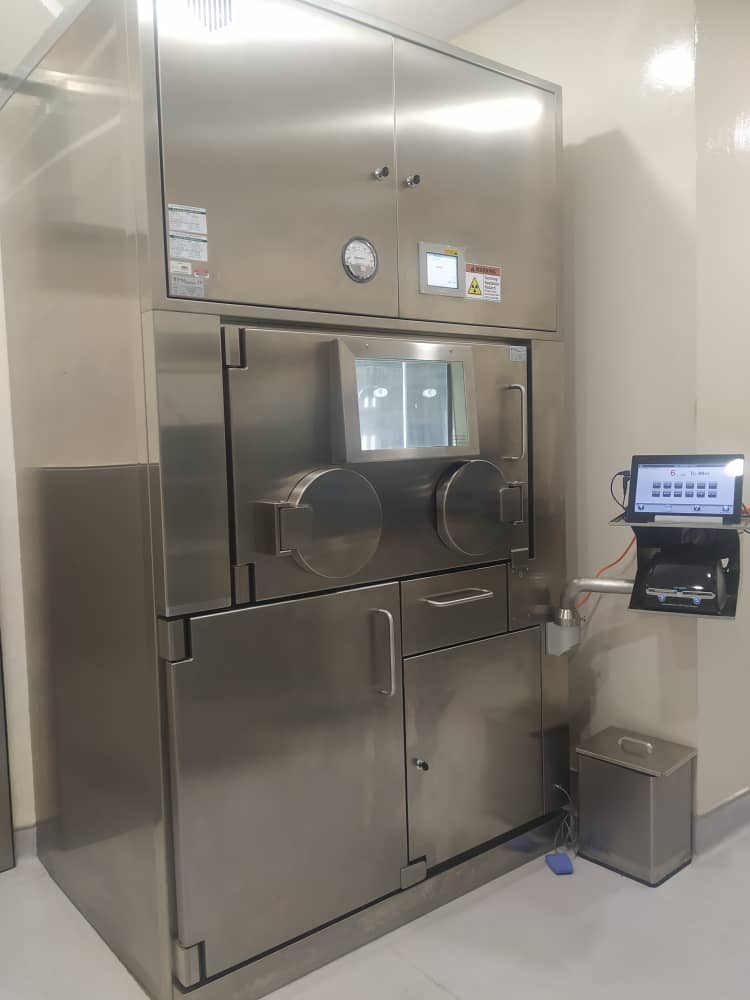
Radiopharmaceuticals laboratory and research service (Hotlab) is one of the sections in the Nuclear Imaging Unit, HSAAS. It is an essential counterpart in ensuring seamless services of nuclear imaging could be provided to patients. This facility is equipped with an isolator (Tema Sinergie NMC PRI 30-10) and a Class I Safety Cabinet (Tema Sinergie FH-1 10) for preparation of sterile pyrogen-free product and non-sterile preparation respectively. Roles of this section includes procurement of radioactive and non-radioactive materials, preparation and dispensing of high quality and safe radiopharmaceuticals for patient use, conducting quality control and quality assurance programme, managing proper storage and disposal of radioactive, biological and general waste as well as assisting in research activities in the unit.
|
| |
Updated:: 07/04/2023 [khairun]
MEDIA SHARING